Gynecomastia in Teenage (GIT)
The teenage years are a time of significant physical and emotional changes, and one issue that can cause distress for many adolescent boys is gynecomastia. Gynecomastia refers to the development of breast tissue in males, and it is more common in teenagers than one might think. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and potential treatments for teenage gynecomastia, as well as discuss the emotional impact it can have on young individuals. By understanding this condition better, we can foster empathy, support affected teenagers, and help them navigate this often challenging period of their lives.
Understanding Teenage Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia, commonly known as “man boobs,” is a condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males. During puberty, hormonal changes can cause an imbalance between estrogen (female hormone) and testosterone (male hormone), leading to the development of breast tissue in males. While this condition often resolves on its own within a few years, it can cause significant distress and embarrassment for teenage boys.
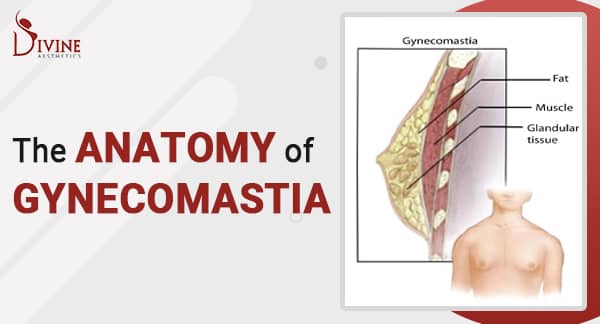
Gynecomastia can usually be categorized under the following categories: true gynecomastia and pseudo gynecomastia. True gynecomastia occurs when the actual breast gland tissue enlarges, while pseudo gynecomastia refers to the accumulation of fat deposits in the chest area, giving the appearance of breasts. Determining the type of gynecomastia is crucial for appropriate treatment and management.
True Gynecomastia vs. Pseudogynecomastia: Understanding the Difference
Gynecomastia is not a one-size-fits-all condition. There are two primary types: true gynecomastia and pseudo gynecomastia. Understanding the distinction between these two forms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
True gynecomastia refers to the enlargement of glandular breast tissue in males. It occurs when there is an overgrowth of breast glandular tissue due to hormonal imbalances. The excess tissue may feel firm or rubbery to the touch. True gynecomastia can affect one or both breasts, and it can lead to nipple tenderness or discharge.
On the other hand, pseudo gynecomastia is characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in the chest area, creating the appearance of breasts. Unlike true gynecomastia, this type does not involve an increase in glandular tissue. Pseudogynecomastia is often associated with weight gain or obesity. It may feel soft and squishy to the touch, and the breast tissue does not typically produce nipple discharge.
Distinguishing between true gynecomastia and pseudo gynecomastia is important because the underlying causes and treatment approaches can differ. While hormonal imbalances are the primary cause of true gynecomastia, pseudo-gynecomastia is usually related to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and overall body fat percentage.
Causes of Teenage Gynecomastia
Several factors contribute to the development of gynecomastia in teenagers. Hormonal imbalances are the primary cause, as testosterone and estrogen regulate the growth and development of breast tissue. During puberty, hormone levels can fluctuate, and the temporary increase in estrogen can lead to gynecomastia.
Medications and Substances That Can Contribute to Gynecomastia
Several medications and substances have been linked to the development of gynecomastia. Understanding the potential triggers can help individuals and healthcare professionals identify potential causes and make informed decisions regarding treatment options.
Certain medications have been associated with gynecomastia as a side effect. These can include:
- Anti-androgens: Medications used to treat prostate cancer, certain prostate enlargement conditions, or transgender hormone therapy can disrupt the balance between estrogen and testosterone, leading to breast tissue growth.
- Anabolic steroids: Abuse of anabolic steroids, often by athletes or bodybuilders seeking to enhance performance, can lead to hormonal imbalances and gynecomastia.
- Anti-anxiety medications: Some benzodiazepines and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) used to treat anxiety and depression may increase the risk of gynecomastia.
- Antibiotics: Certain antibiotics, such as ketoconazole and isoniazid, have been associated with gynecomastia in rare cases.
In addition to medications, certain substances can also contribute to the development of gynecomastia. These substances include:
- Marijuana: Regular use of marijuana, especially during adolescence when hormonal fluctuations are already occurring, has been linked to an increased risk of gynecomastia.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt hormone levels and contribute to the development of gynecomastia.
- Illicit drugs: Substances like amphetamines, heroin, and methadone have been associated with gynecomastia.
It is important to note that not everyone who takes these medications or uses these substances will develop gynecomastia. However, if gynecomastia symptoms arise, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional to evaluate the potential underlying causes.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Teenage Gynecomastia
Recognizing the symptoms of gynecomastia is crucial for early detection and intervention. By understanding what to look for, teenagers and their parents or guardians can seek appropriate medical guidance and support.
The most common symptom of gynecomastia is the enlargement of breast tissue. This can manifest as a firm or rubbery mass beneath the nipple area. In some cases, the breast tissue may be tender or sensitive to touch. It is important to note that gynecomastia can occur on one or both sides of the chest.
Other symptoms that may accompany gynecomastia include
- Nipple discharge: In rare cases, gynecomastia may cause discharge from the nipples. This discharge can be clear, white, yellowish, or bloody. If nipple discharge is present, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation.
- Psychological distress: Gynecomastia can significantly impact a teenager’s emotional well-being. Feelings of self-consciousness, embarrassment, and lowered self-esteem are common. Teenagers may withdraw from social activities, experience depression or anxiety, and have body image concerns.
If a teenager experiences any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can conduct a physical examination, assess the individual’s medical history, and provide appropriate guidance and support.
Emotional Impact of Teenage Gynecomastia
Teenage gynecomastia is characterized by swollen breast tissue, tenderness, and sometimes nipple discharge. Adolescents experiencing these symptoms may feel self-conscious, embarrassed, and anxious about their physical appearance. Negative body image and lowered self-esteem are common emotional consequences of gynecomastia, potentially leading to social withdrawal and even depression.
Addressing Teenage Gynecomastia
While teenage gynecomastia often resolves without medical intervention, supportive measures can help alleviate the emotional distress associated with this condition. Here are some strategies for addressing teenage gynecomastia:
- Education and Counseling: Providing comprehensive information about gynecomastia can help teenagers understand that it is a common condition and usually temporary. Counseling sessions can also help individuals cope with body image issues and improve self-confidence.
- Supportive Environment: Creating a supportive and understanding environment at home, school, and social circles can go a long way in helping teenagers feel accepted and comfortable with their bodies. Encouraging open conversations and promoting body positivity can make a significant difference.
- Lifestyle Changes: Encouraging a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can help reduce excess body fat and improve overall body composition. However, it’s essential to approach these changes with sensitivity and avoid placing undue pressure on teenagers.
- Medical Intervention: In rare cases where gynecomastia persists or causes severe emotional distress, medical intervention may be considered. Options include hormonal therapy to rebalance hormone levels, surgical removal of excess breast tissue, or liposuction for pseudo-gynecomastia.
Addressing teenage gynecomastia Surgically
Gynecomastia procedure, also known as male breast reduction surgery, is a surgical intervention designed to treat gynecomastia in teenagers. The procedure involves the removal of excess glandular tissue and fat from the male chest to create a more contoured and masculine appearance. The surgical technique employed will depend on the specific characteristics and severity of gynecomastia in each individual case. In some instances, liposuction may be sufficient to address excess fatty tissue, while in other cases, surgical excision may be necessary to remove glandular tissue. The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia, and the surgeon will make discreet incisions to access and remove the targeted tissue. Following the surgery, the incisions are closed with sutures, and patients are usually required to wear compression garments to support healing and optimize results. Gynecomastia surgery can be an effective solution for teenagers with persistent gynecomastia that causes significant physical and psychological distress, helping them achieve a more masculine chest contour and improve their self-esteem. However, it is important for teenagers and their parents or guardians to consult with a qualified plastic surgeon and thoroughly understand the procedure, potential risks, and recovery process before making a decision.
Conclusion
Teenage gynecomastia is a common yet often misunderstood condition that can significantly impact the emotional well-being of affected individuals. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and potential treatments of gynecomastia, we can support teenagers in navigating this challenging period in their lives. Educating teenagers, fostering a supportive environment, promoting healthy lifestyle choices, and, in some cases, considering medical interventions can help alleviate the distress associated with gynecomastia. It’s crucial for society to be more empathetic and supportive, ensuring that adolescent boys feel comfortable and confident in their own bodies, irrespective of their physical appearance.
FAQs
Q: Is gynecomastia common among teenagers?
A: Yes, gynecomastia is relatively common during adolescence. It is estimated that up to 65% of boys experience some degree of breast tissue enlargement during puberty. However, the majority of cases resolve on their own without any intervention.
Q: How can I differentiate between true gynecomastia and pseudo gynecomastia?
A: True gynecomastia involves the enlargement of glandular breast tissue, while pseudo gynecomastia is characterized by an accumulation of excess fat in the chest area. A medical professional can help determine the underlying cause through physical examination and, if necessary, imaging tests.
Q: Will gynecomastia go away on its own in teenagers?
A: In many cases, gynecomastia in teenagers resolves spontaneously within a few months to a couple of years as hormone levels stabilize. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to monitor the condition and ensure appropriate management.
Q: Can medications or substances cause gynecomastia in teenagers?
A: Yes, certain medications and substances have been linked to the development of gynecomastia. Medications such as anti-androgens, anabolic steroids, and certain antidepressants can contribute to the condition. Substance use, including marijuana and excessive alcohol consumption, has also been associated with gynecomastia.
Q: What are the non-surgical treatment options for teenage gynecomastia?
A: Non-surgical options for managing gynecomastia include lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and weight management. In some cases, hormonal therapy may be prescribed to address hormonal imbalances contributing to gynecomastia.
Q: When is gynecomastia surgery recommended for teenagers?
A: Gynecomastia surgery is typically considered for teenagers who have persistent gynecomastia that causes significant physical and psychological distress. It is important to consult with a qualified plastic surgeon to determine if surgical intervention is the most appropriate course of action.